What Is A Marginal Change
Marginal Analysis
Compares the additional benefits derived from an activity and the extra price incurred past the same activity
What is Marginal Analysis?
Marginal analysis compares the boosted benefits derived from an activity and the extra cost incurred by the aforementioned activity. Information technology serves as a conclusion-making tool in projecting the maximum potential profits for the visitor by comparing the costs and benefits of the activity.
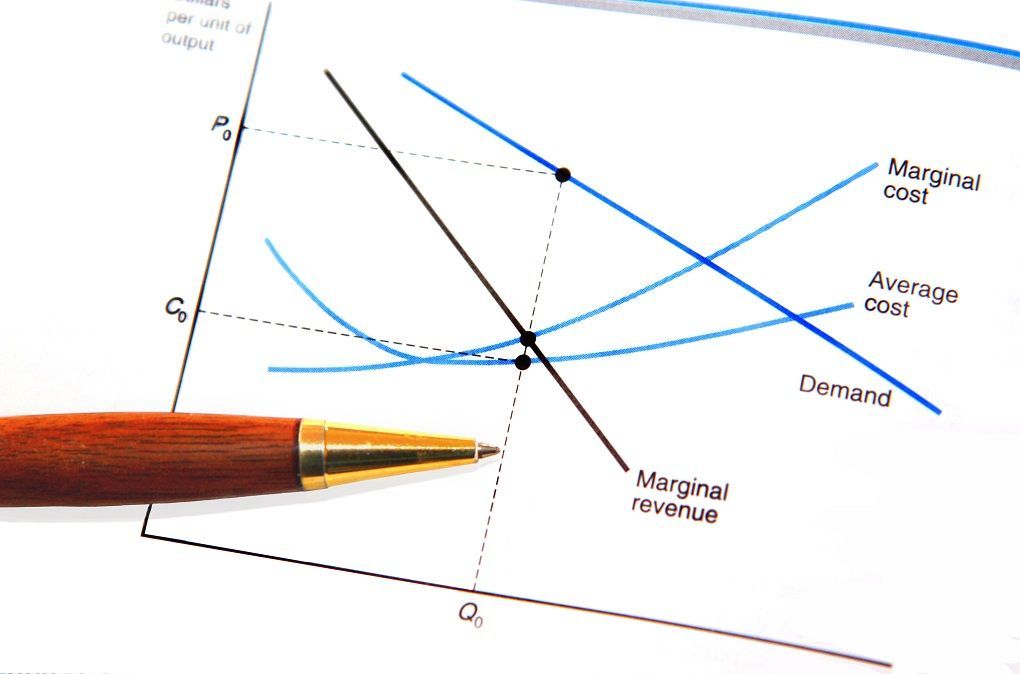
The term "marginal" is used by economists to refer to the changes resulting from one unit of measurement change in activity. It is concerned with the incremental cost and benefit stemming from a modify in production.
Summary
- Marginal analysis a controlling tool used to examine the additional benefit of an activity contrasted with the extra cost incurred by the same activeness.
- Information technology is mostly used by companies to maximize efficiency and better their decision-making processes.
- The marginal analysis of costs and benefits is necessary, especially for a visitor planning to expand its business organization operations.
Agreement Marginal Analysis
In microeconomics , most decisions usually evaluate whether the do good of a detail activity or activeness is greater than the cost. Marginal analysis comes in handy when making a decision with a causal relationship involving two variables. Information technology explains the potential effect of some conditional changes on a company as a whole.
Past examining the associated costs and potential benefits, marginal analysis provides useful data that is probable to prompt price or product change decisions.
Marginal analysis also looks at the atmospheric condition under which the company may continue with the same toll of producing an private unit or output in the face of expected or bodily changes. Here, the dominating principle is the aligning to alter. The thought is that it is worthwhile for a company to continue investing until the marginal revenue from each actress unit is equal to the marginal cost of producing it.
Marginal assay may also be applied in a situation where an investor is faced with two potential investments but with the resources to but invest in one. The investor can use marginal assay to compare the costs and the benefits of both investments to determine the option with the highest income potential.
Uses of Marginal Analysis
The following are the two prevalent uses of marginal analysis:
1. Observed changes
Marginal analysis tin exist used by managers to create controlled experiments based on the observed changes of particular variables. For example, the tool tin can be used to evaluate the impact of increasing production at a given percentage on cost and revenues.
A do good is accrued when the marginal cost is reduced or the increased revenues cover and spill over full product costs. If the experiment yields a positive result, incremental steps are taken until the upshot yields a negative event. This may be the scenario when the market cannot take the additional production units, leading to excessive overheads. At that stage, a company with the capacity to aggrandize will opt to increase its market accomplish.
2. The opportunity cost of an activity
Managers regularly find themselves in situations where they are required to make a choice amid available options. For example, suppose a company has a single job opening, and they have the choice of hiring a inferior administrator or a marketing director.
Marginal assay may betoken that the company has resources to grow and that the market is saturated. As a result, hiring a marketing director will yield college returns than an administrator.
Rules of Marginal Analysis in Decision-Making
There are two rules for profit maximization that make marginal assay a key component in the microeconomic analysis of decisions. They are:
i. Equilibrium Rule
The start rule posits that the activity must exist carried out until its marginal price is equal to its marginal acquirement . The marginal profit at such a point is zero. Typically, turn a profit can be increased by expanding the activeness if the marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost.
Marginal benefit is a measure out of how the value of cost changes from the consumer side of the equation, while the marginal cost is a measure of how the value of cost changes from the producer side of the equation. The equilibrium rule implies that units will exist purchased upwards to the point of equilibrium, where the marginal acquirement of a unit of measurement is equal to the marginal cost of that unit.
2. Efficient Allocation Dominion
The second rule of profit maximization using marginal assay states that an activity should be performed until it yields the same marginal return for every unit of measurement of endeavor. The rule is premised on the thought that a visitor producing multiple products should classify a gene between ii product activities such that each provides an equal marginal profit per unit of measurement.
If it is not achieved, profit could exist realized by allocating more input to the activity with the highest marginal profit and less to the other activity.
Limitations of Marginal Assay
I of the criticisms confronting marginal assay is that marginal data, by its nature, is usually hypothetical and cannot provide the true pic of marginal toll and output when making a decision and substituting appurtenances. It therefore sometimes falls short of making the best conclusion, given that most decisions are made based on average data.
Another limitation of marginal analysis is that economic actors make decisions based on projected results rather than actual results. If the projected income is non realized as predicted, the marginal analysis volition prove to exist worthless.
For example, a company may decide to kickoff a new product line based on a marginal analysis project that the revenue will exceed costs to establish the production line. If the new production line does not meet the expected marginal costs and operates at a loss, it ways that the marginal analysis used the wrong assumptions.
Special Considerations
Marginal analysis may also apply to the effects of small changes and the opportunity cost concept. In the sometime, marginal assay relates to observed changes with total outputs. Evaluating such changes tin can help determine the standard production rate.
It is common in employment scenarios, where the Human Resources (HR) manager makes a hiring determination. Suppose a company'due south upkeep allows the recruitment of i employee. With marginal analysis, the HR tin know whether an additional employee in the product department provides net marginal do good.
Additional Resources
CFI is the official provider of the global Capital Markets & Securities Analyst (CMSA)® certification plan, designed to assistance anyone become a earth-grade financial analyst. To keep advancing your career, the boosted CFI resource below volition exist useful:
- Marginal Profit
- Marginal Toll Formula
- Profit Margin
- Economic science of Production
What Is A Marginal Change,
Source: https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/knowledge/economics/marginal-analysis/
Posted by: simonsdecten.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Is A Marginal Change"
Post a Comment